Use of shadows keyword in VB.NET
.NET, Shadows, VB.NET, Visual Basic 2010
In this article We will learn how to use shadows in VB.NET.
Shadows:
Use shadows to define method hiding explicitly. If There are overloaded methods in the base class and you marks one of the methods as shadows using the keyword shadow in the derived class, then we cannot access the overloaded methods. OR the child member temporarily hides the parent member and activates its own. This is called shadowing. The purpose of shadows is to Protects against a subsequent base-class modification that introduces a member you have already defined in your derived class.If you do not specify either Shadows or Overrides, the compiler issues a warning message to help you be sure which kind of redefinition you want to use. If you ignore the warning, the shadowing mechanism is used.
Module Module1
Class A
Public Sub Show()
Console.WriteLine("Calling from A")
End Sub
End Class
Class B
Inherits A
Public Shadows Sub Show()
Console.WriteLine("Calling from B")
End Sub
End Class
Class C
Inherits B
Public Shadows Sub Show()
Console.WriteLine("Calling from C")
End Sub
End Class
Class Test
Public Shared Sub Main()
Dim x As A
x = New A()
x.Show()
x = New B()
x.Show()
x = New C()
x.Show()
End Sub
End Class
End Module
OUTPUT:
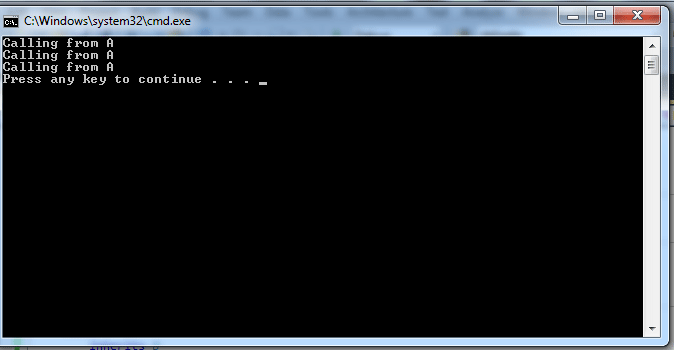
If we do not use the shadows keyword in the derived class it gives an warning at compile time but does not effect at the run time.